The difference between IO-Link Class A and Class B
The IO-Link protocol has two types of ports: Class-A and Class-B. The physical interface codes of the two are the same, both belong to A-CODE, and the communication protocols are essentially the same. The difference is that the pin definitions and load capacities are different.
1. Class-A (Class A port)
There is only one set of US power supply, which has weak load capacity and can only carry input modules or some low-power output loads. Pin 2 is a manufacturer-defined pin, which can be designed as an additional DI/DO channel. When configured as DO, the master station will transmit UA power, which can increase the output load capacity, similar to a Class B port. The specific pin definitions are as follows:
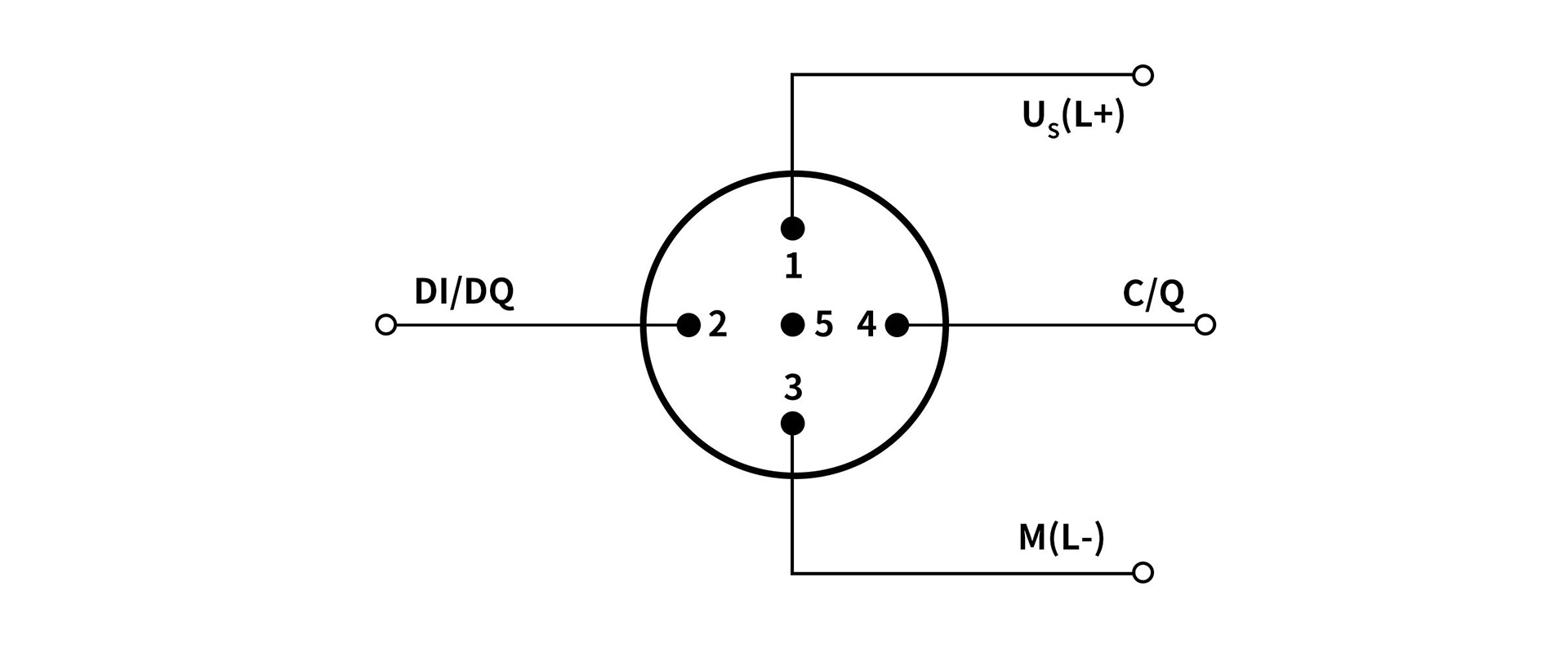
PIN1-Us: Provides system power 24V+
PIN2-Manufacturer-defined: Used as DI for 01 series products of Solidot Technology
PIN3-GNDs: Provides system power 0V
PIN4-DI/DQ/IO-Link
PIN5 - Not used
2. Class-B (Class B port)
There is an additional power supply for higher current load scenarios. The specific pin definitions are as follows:
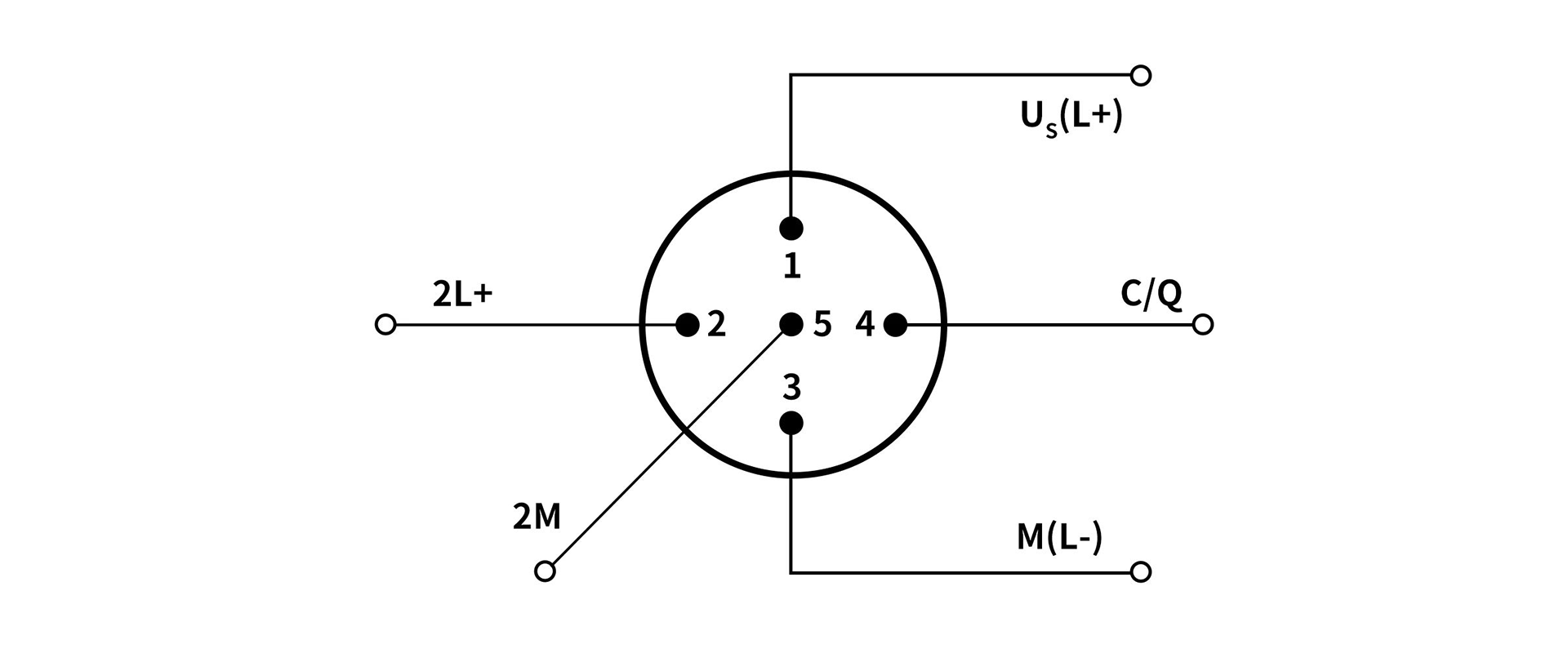
PIN1-Us: Provides system power 24V+
PIN2-Ua: Provide auxiliary power 24V+
PIN3-GNDs: Provides system power 0V
PIN4-DI/DQ/IO-Link
PIN5-GNDa: Provide auxiliary power 0V
Class A ports can meet the needs of applications in most scenarios, such as commonly used digital I/O slaves, various sensors, alarm lights, RFID, etc. These products generally only need Us power supply.
Products with Class B ports are generally used for high-power actuators, such as solenoid valves. In this case, Us provides system power and Ua provides auxiliary power for the solenoid valve coil to be attracted.